GROUPS OF ORGANISMS
|
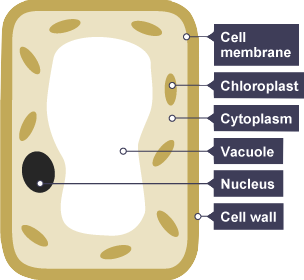
PLANTS
s
- Nucleus - membrane-bound organelle containing chromosomes
- Chloroplast - protein to carry out Photosynthesis
- Mitochondria - protein to carry out cell respiration
- Cytoplasm - fills the cell to facilitate chemical reactions and holds organelles in place
- Vacuole - storage organelle for Water and dissolved substances
- Cell membrane - phospholipid bilayer that controls movement of substances into and out of cell
- Cell wall - made of Cellulose to protect and maintain the shape of cell
- Example: Herbaceous Legume
|
 |
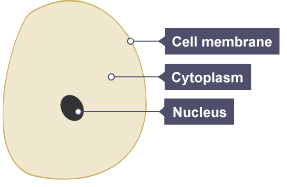
ANIMALS
s
- Nucleus - membrane-bound organelle containing chromosomes
- Mitochondria - protein to carry out cell respiration
- Cytoplasm - fills the cell to facilitate chemical reactions and holds organelles in place
- Cell membrane - phospholipid bilayer that controls movement of substances into and out of cell
s
|
 |
FUNGI
s
Both multicellular and unicellular
Stores carbohydrates as Glycogen
Organised into a Mycelium - thread-like structure called Hyphae that contains many Nuclei
- Nucleus - membrane-bound organelle containing chromosomes
- Mitochondria - protein to carry out cell respiration
- Cytoplasm - fills the cell to facilitate chemical reactions and holds organelles in place
- Cell membrane - phospholipid bilayer that controls movement of substances into and out of cell
|
 |
PROTISTS
s
|
|
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteWow! this is really cool explanations with the images. As I am a biological student I used to follow https://typicalstudent.org/ where I found really resourceful information for students.
ReplyDeleteWhen it says 'threat-like structure' is it meant to say thread-like structure? Correct me if i'm wrong but I feel like this is a mistake. Thank you for your consideration.
ReplyDeleteno shit sherlock
DeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
Deletethe guy wrote it right retard
Deleteis there a cell wall in the fungi because in the diagram there is and in the writing there isn't
ReplyDeletenice
ReplyDeleteThanks for the blog filled with so many information. Stopping by your blog helped me to get what I was looking for 인싸홀덤
ReplyDelete. Now my task has become as easy as ABC 인싸포커 .
Greetings! This is my first visit to your blog! Your blog provided us beneficial information to work on. I really love all that have been posted here and it gives me a lot of new information regarding all the subjects I needed. Thank you for sharing your ideas to others. 비트코인
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteWOW! this is clear, concise, and complete quality stuff you are delivered here. Role of Digital learning in education
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteAwesome post Great share! Useful post Amazing write-up! Keep posting thanks for sharing
Deleteiv vitamin therapy
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeletechlorella
ReplyDeleteslot
ReplyDeleteslot88
slot online
slot gacor
slot gacor hari ini
slot online gacor
judi slot
judi slot online
situs slot
situs judi online
https://pulltogether.org
Thanks For Sharing..!
ReplyDeleteEmerge212 Small Business Advice_ How To Collaborate Effectively With Your Colleagues
ReplyDeleteYou definitely have some great insight and great storie. rajatarung
ReplyDeleteYou definitely have some great insight and great storie. link rajatarung
ReplyDelete